Two ways I discovered to pass dynamic (arrow and non-arrow) function parameters
In my attempt to understand how the clsx utility is written by looking at its source code, I found that clsx does not have function parameters declared.

How is it possible to access the parameters without declaring them? clsx expects dynamic parameters. Below is an usage example from the docs
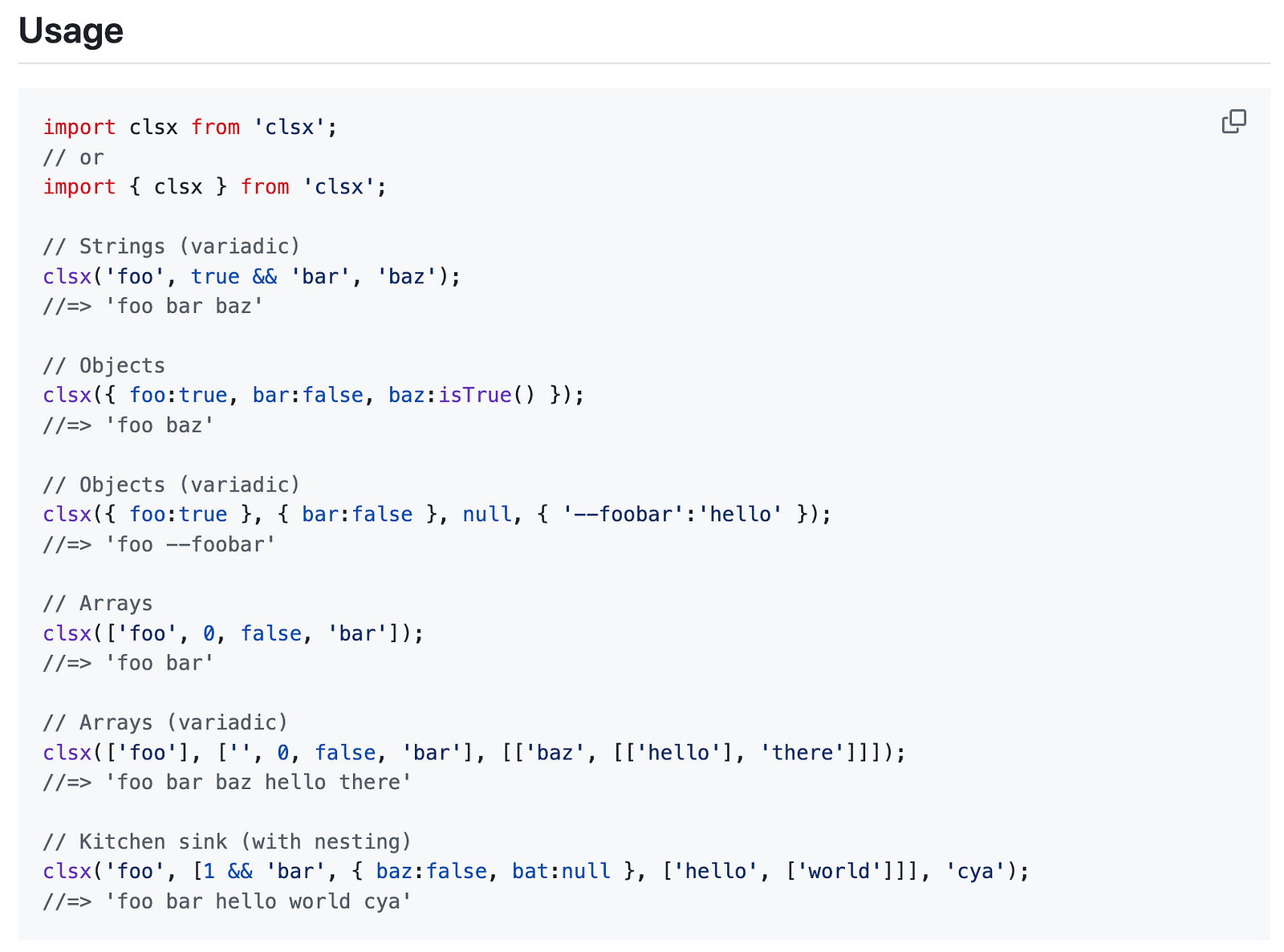
Then, I looked at the function code and from the lines below, it was apparent that through arguments variable, it is possible to access the function parameters.
export function clsx() {
var i=0, tmp, x, str='', len=arguments.length;
I searched on Google with this query “arguments without paramters in nodejs” and clicked on the first Stackoverflow link.
argumentsis an Array-like object accessible inside functions that contains the values of the arguments passed to that function.The
argumentsobject is a local variable available within all non-arrow functions.
First way of accepting dynamic function parameters (non-arrow):
The
argumentsobject is useful for functions called with more arguments than they are formally declared to accept. This technique is useful for functions that can be passed a variable number of arguments.
Using arguments only works in non-arrow functions.
Second way of accepting dynamic function parameters (arrow):
I read in some open source code sometime ago (I think, it is nextjs source code), don’t exactly remember but, you could use spread operator to accept dynamic function parameters. I found this stackoverflow question.
const childFunc = (str1, str2, str3) => `${str1} ${str2} ${str3}`;
const parentFunc = (...args) => childFunc('foo', ...args);
console.log(parentFunc('bar', 'fizz'));
Since arguments variable does not work in arrow functions, I would choose a spread operator like shown in the above code snippet.
Conclusion:
Use arguments in non-arrow functions and a single parameter with a spread operator in arrow functions to accept dynamic function parameters.
